We have recently
experienced the earthquake(25 april-2015 & 12 may-2015), the epicenter was
in Nepal.(7.9 magnitude &7.3 magnitude respectively).so, let’s take a look
on earthquakes…
- What is earthquake??
Earthquakes
are usually caused when rock underground suddenly breaks along a fault. This
sudden release of energy causes the seismic waves that make the ground shake.
When two blocks of rock or two plates are rubbing against each other, they
stick a little. They don't just slide smoothly; the rocks catch on each other.
The rocks are still pushing against each other, but not moving. After a while,
the rocks break because of all the pressure that's built up. When the rocks
break, the earthquake occurs. During the earthquake and afterward, the plates
or blocks of rock start moving, and they continue to move until they get stuck
again. The spot underground where the rock breaks is called the focus of the
earthquake. The place right above the focus (on top of the ground) is called
the epicenter of the earthquake
Fault or fault plane = the surface where when
two blocks of the earth suddenly slip past one another
Hypocenter = the location below the earth’s surface where the earthquake starts
Epicenter = the location on the surface of the earth directly above the hypocenter
Hypocenter = the location below the earth’s surface where the earthquake starts
Epicenter = the location on the surface of the earth directly above the hypocenter
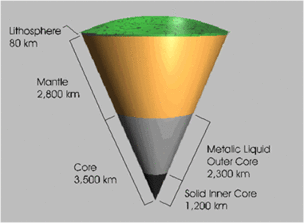
- Composition of earth
The
earth has four major layers: the inner
core, outer core, mantle and crust.
The crust and the top of the mantle make up a thin skin on the surface of our
planet. But this skin is not all in one piece , it is made up of many pieces
like a puzzle covering the surface of the earth. Not only that, but these
puzzle pieces keep slowly moving around, sliding past one another and bumping
into each other. We call these puzzle pieces tectonic
plates, and the edges of the plates are called the plate boundaries.
- Where Do Earthquakes Happen?
Most
earthquakes occur along the edge of the oceanic and continental
plates. The plates are moved around by the motion of a deeper part of the
earth (the mantle) that lies underneath the crust. These plates are
always bumping into each other, pulling away from each other, or past each
other. The plates usually move at about the same speed that your fingernails
grow. Earthquakes usually occur where two plates are running into each other or
sliding past each other.
Earthquakes
can also occur far from the edges of plates, along faults. Faults are
cracks in the earth where sections of a plate (or two plates) are moving in
different directions. Faults are caused by all that bumping and sliding
the plates do. They are more common near the edges of the plates.
Types of fault
Normal
faults are the
cracks where one block of rock is sliding downward and away from another block
of rock.
 |
| normal fault |
Reverse
faults are
cracks formed where one plate is pushing into another plate At these faults,
one block of rock is sliding underneath another block or one block is being
pushed up over the other.
 |
| reverse fault |
Strike-slip
faults are the
cracks between two plates that are sliding past each other.
 |
| strike-slip fault |
- Seismic zones of India
The
Indian subcontinent has a history of devastating earthquakes. Geographical statistics of
India show that almost 54% of the land is vulnerable to earthquakes. Seismic
Zonation map of a country is a guide to the seismic status of a region and its
susceptibility to earthquakes. India has been divided into five zones with
respect to severity of earthquakes
Zone
5 : This regions in Zone 5 not only experience frequent earthquakes, but these
earthquakes are devastating ones. The earthquakes that occur here have the
highest intensity than recorded at other parts of the country. The entire state
of Kashmir falls in this area. Western Himalayas are also classified as Zone 5.
Some North-East Indian cities such as North Bihar Guwahati fall in this area.
The Rann of Kutch is classified as Zone 5.
Zone4:
Also called the High Damage Risk Zone, Zone 4 is an area that has the highest
possibilities of earthquakes of a large magnitude. Delhi falls in this zone.
Southern parts of Kashmir also fall in Zone 4
Zone
2:The regions in Zone 2 are less likely to be affected by earthquakes. These
cities, towns, rural areas, and villages experience earthquakes very rarely.
Zone 3 :This Zone has
moderate risk. Some areas in the Western Himalayas, Kashmir, and Andaman &
Nicobar Islands fall in Zone 3
- Worst earthquakes in India
Indian Ocean Earthquake, 2004
Date - December 26, 2004
Time
- 08:50
|
|||||||||||||
Deaths
- > 283,106 (Includes deaths in Indonesia, Sri Lanka, India, Thailand,
Maldives, and Somalia)
|
|||||||||||||
BEFORE :
The effective disaster prevention is planning:
ü Know
the earthquake hazards in your area.
ü Follow
the structural desin and engineering practices when constructing houses and
building.
ü
Evaluate the structural soundness of buildings and houses;
strengthen or retrofit if necessary
Prepare
your homes ,workplace or schools:
ü Strap
or bolt heavy furnitures cabinets to the walls
ü Check
the stability of hanging objects like ceiling fans and chandelirs
ü Breakable
items, harmful chemicals and flammable materials should be
stored properly in the lowermost secured shelves.
Familiarize yourself
with the exit routes. Know where the fire extinguishers , first aid kit, alarms,
communication facilities are located .Learn how to use them before hand.
Prepare a handy emergency supply kit with first aid kit, canned food and can
opener ,water , clothing, blanket,
battery-operated ,radio, flashlights and extra batteries. Conduct and participate in regular earthquake drills.
DURING :
Stay Clam.
When you are inside a structurally sound building or home…
STAY THERE!
ü If
possible quickly open the door for exit.
ü Duck
under a study table or desk and hold on to it, or protect your head with arms.
ü Stay
away from glass windows shelves cabinetsand other heavy objects.
ü Beware
of falling objects.Be alert and keep your eyes open.
If you are outside…move to an open areal…
ü Stay
away from trees powerlines, posts and concrete structure
ü Move
away from steep slopes which may be affected by landslides.
ü If
you are near the shore and feel earthquake, especially if it is too strong move
quickly to higher grounds .Tsunamis might follow.
ü If
you are in amoving vechile ,STOP and get out. Do not cross overpasses ,cross
bridges or flyovers which may have been damaged.
AFTER
Be prepared for aftershocks. Once the shaking
stops, take the fastest and safest way out of the building.
DON’T
ü Use elevators
ü Enter
damaged buildings
ü Use
telephones unless necessary.
ü PANIC
CHECK
ü Yourself
and others for injuries.
ü Water
and electrical lines for damages
ü For
spills of chemical toxic and flammable
fires which may spread.
ü And
control fires which may spread.
If
you need to evacuate your residence, leave a message where you are going and
bring your emergency supply kit. Keep updated on disaster prevention
instructions from battery-operated radios.
REFERENCES……
|

No comments:
Post a Comment